1. COURSE DESCRIPTION
The course provides a comprehensive overview of CSV (Creating Shared Value) concepts and how businesses can address social needs while benefiting both the firm and society. It covers value creation, collaboration, and assessing a business’s impact on social needs. Case studies explore ethical behavior and the consequences of irresponsible actions. Major case studies demonstrate how addressing social needs aligns with profit objectives and opens up new opportunities. Additional case studies analyze smaller-scale examples. The course discusses CSR, philanthropy, and the Social Progress Index. Students evaluate companies using the CSV framework and engage in group work and online interaction. The course aims to instill key principles of creating shared value and ethical behavior while recognizing underserved social needs as opportunities for competitive advantage.
2. REASON FOR THE COURSE
This course introduces students to Creating Shared Value (CSV), which combines addressing social needs with making a profit and creating sustainable competitive advantage. It differentiates CSV from CSR and philanthropy by integrating social needs directly into the business model. Students assess CSV as both an ethical and profitable approach, using frameworks to recognize how businesses can contribute to society. The course explores company responsibilities and opportunities to address social needs, developing students’ ethical understanding and reasoning abilities. By considering social needs and ethical issues, students can make informed decisions and build strategic solutions that align business opportunities with social impact.
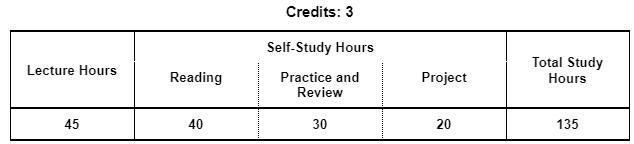
3. STUDY HOURS
4. ROLE IN CURRICULUM

Prerequisite:
Students must have finished Principles of Management before attempting this course.
The course begins with a thorough overview of CSV Concepts to show how businesses can be involved in addressing social needs, and how this might be done (including CSV at Level 1, 2 and 3). A case study focusing on ethical behaviour in practice, British American Tobacco selling cigarettes in Africa, provides a reference point for the ethics of business practices. This is followed three major case studies (Intercorp, Discovery and Walmart) which are covered and assessed in detail to show how some large and well known businesses have found that addressing social needs, and how this has been entirely consistent with profit objectives and has opened up new opportunities and markets based on on addressing social needs that had previously been underserved. Two further frameworks are discussed in detail during the course. Firstly, CSR and Philanthropy, which along with CSV provide the spectrum of methods that companies have used to contribute to social needs. Secondly, the Social Progress Index is assessed in detail to provide a framework for identifying social needs and assessing the progress of countries worldwide in addressing these social needs.
Further case studies are introduced during the course either as a detailed analysis or at overview level. These include both international and more local case studies focusing on usually smaller scale Cambodian and/or ASEAN examples. The students’ assignment involves the students working in groups to identify local, or international companies which have stated an intention to address social needs as a core part of their business so that students can assess these companies under the same CSV framework. Some of these examples are further developed into case studies which can be used for future teaching in the course. A further case study, the Aberfan disaster, South Wales (1966) is shown as an early example where little responsibility was taken to avert a mining disaster, and which has served as an example of the need for responsible behaviour since that time. It is also used to compare the region as it was at the time of the disaster with how it has prospered today. All in all, the course provides a comprehensive framework under which to determine the role that business can play in society, and in particular to demonstrate that Creating Shared Value is a legitimate and well proven strategy. The case studies, examples and the student assignment are all used to provide examples either to show how CSV can work or to compare with other forms of ethical and less ethical strategies.
The quizzes and assignments focus on requiring the students to consider all the commercial and ethical issues involved and gain an understanding of the context of creating shared value. Group work and online interaction to focus on these issues are integral to the course and the student group assignment is an opportunity for students to gain an understanding based on real life interviews with companies in Cambodia. Students are required to reflect carefully and profoundly on ethical issues. By the end of the course, they are expected to internalise key principles of creating shared value and the wider issues of ethical and professional behaviour as well as being able to understand how creating shared value requires a strongly commercial approach and recognition of underserved social needs that create opportunities for sustainable competitive advantage.
Credits: 2
Lecture Hours: 45
Self-Study Hours:
Total Study Hours: 135

Prerequisite
Students must have finished Principles of Management before attempting this course.
On successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
1 Knowledge
| Level of Learning | PLO | CLO | Learning Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Understand | PK2, PK4 | CK1 | Explain and show cases where ethical and unethical practices in business impact the wider community |
| Understand | PK2, PK4 | CK2 | Explain the conceptual framework involved in Creating Shared Value |
2 Cognitive Skills
| Level of Learning | PLO | CLO | Learning Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluate | PK2 PK4 PC5 | CC1 | Assess successful Creating Shared Value strategies both their impact on the business and the wider impact on the social needs being addressed. |
| Evaluate | PK2 PK4 PC5 | CC2 | Assess the extent to which Creating Shared Value is consistent with Corporate Social Responsibility and Philanthropy. |
| Apply | PK2 PK4 PC5 | CC3 | Apply the framework and principles used in the Social Progress Index (and other relevant indices) to identify appropriate social needs that companies might address. |
3 Communication, Information Technology, and Numerical Skills
| Level of Learning | PLO | CLO | Learning Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apply | PK2 PK4 PC5 PCIT4 | CCIT1 | Use a case study to discuss how business solutions can contribute to social needs, and associated ethical issues in business. |
4 Interpersonal Skills and Responsibilities
| Level of Learning | PLO | CLO | Learning Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluate | PIP1 PIP2 PIP3 | CIP1 | Determine the Creating Shared Value approach with the same degree of professionalism. |
The course targets the 30 lessons in the study plan below. Each lesson is 1.5 class hours each; there are a total of 45 class hours. The study plan below describes the learning outcome for each lesson, described in terms of what the student should be able to do at the end of the lesson. Readings should be done by students as preparation before the start of each class. Implementation of this study plan may vary somewhat depending on the progress and needs of students.
This course covers three main conceptual areas, Creating Shared Value, Corporate Social Responsibility and Social Progress, each of which are covered in detail to the point where students can use these concepts to analyse their impact and recommend policy and actions. Case studies are used to show how ethical issues in business impact society, how social needs are identified, and how shared value can be created. Some of the case studies are assessed in detail and some as an overview. The case studies are both international and local to Cambodia and the ASEAN Region, and range from global corporations to small scale community projects. The case studies are presented in class with interactive quizzes to allow students to understand concepts and to provide them with opportunities to reflect on the issues and their impact, and to put forward their opinions as to the importance and impact of ethical issues, and how creating shared values can apply. Assigned readings are provided to support the learning and to provide additional material to that covered in class. Students are encouraged more and more to read outside of class to augment their understanding and abilities to evaluate concepts and case studies in real life. Student group work is presented in class. The opportunity for individual or group advice is available any time during the semester, and is encouraged.
Grades will be determined based on a grading score, calculated using the following assessments and score allocations:
| Assessment | Weight of each assessment | Learning Outcome Assessed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLO | PLO | ||
| Participation | 20% | CK1, CK2, CC1, CC2, CC3, CCIT1, CIP1 | PK2, PC5, PCIT4 PIP1, PIP2, PIP3 |
| Assignments | 25% | CC1, CC2, CC3, CCIT1, CIP1 | PK2, PC5, PCIT4 PIP1, PIP2, PIP3 |
| In-class tests | 25% | CK1, CK2, CC1, CC2, CC3 | PK2, PC5, PCIT4 |
| Assignments | 15% | CC2, CC3, CIP1, CIP2, CCIT1 | PCIT1, PCIT 2 |
| Final exam | 30% | CK1, CK2, CC1, CC2, CC3, CCIT1 | PK2, PC5, PCIT4 |
| Total grading score | 100% | ||
Assignment The students will be required to undertake one assignment during the course from either of the following (Assignment 1 or Assignment 2).
Assignment 1 – Case Presentation
| Work Group: | Group |
| Output format: | APA Format Report, Presentation |
| Language: | English |
| Assignment: | Each group of students will be required to present one of the CSV course case studies, including the background to the case study, the CSV strategy adopted by the company, how this integrates into the three levels of CSV (Level 1, 2 or 3), how this builds sustainable competitive advantage whilst at the same time addressing ethical issues of business. The assignment should submit what they have presented in class as a short written report. |
Assignment 2 – Company Interview and Report
| Work Group: | Group |
| Output format: | Presentation |
| Language: | English |
| Assignment: | Each group of students will be required to visit a company of their choice to interview the company owner or manager, to determine their view of CSV and the extent to which CSV can lead to sustainable competitive advantage. The format of the interview will be designed in class with student participation so that each group of students will be able to collect similar data from interviews. The results will be presented in class by the students and marked in terms of both content and presentation. |
This course is based on case studies made available by Harvard Business School ‘Creating Shared Value’ Course. These are supported by journal articles on Corporate Philanthropy, Corporate Social Responsibility and Creating Shared Value. These are listed below.
Core Textbooks
Harvard Business School Case Studies for Creating Shared Values
Additional References
The following are journal articles by Harvard Business School, which are specifically used for the Creating Shared Value Course.