1. COURSE DESCRIPTION
Finance 2 prepares students for business finance manager roles. The course begins by explaining the role and purpose of financial management in a business. The course covers investment, financing, and dividend policy, as well as the three fundamental financial management decisions. The next section examines working capital and long-term investments. The next section examines business funding sources like dividend policy and internally generated finance. The cost of capital and other factors influence the choice of capital by the business. In addition, the course covers the valuation of the business and financial assets and their impact on the cost of capital. At the end of the course, we examine the risk and the main techniques used to manage it.
2. REASON FOR THE COURSE
Building on Finance 1 (FFM) and Management Accounting (F2), Finance 2 examines the theory and practice of corporate investment and financial decisions. It aims to explain some key corporate finance decision problems, such as working capital management, long-term capital investment to replace productive assets, financing of short-term and long-term assets, and dividend policy. Students will learn how financial principles and theories apply to real-world challenges organizations face, concentrating on the financial manager’s position and the abilities needed to make good investment and financing decisions. Corporate financial decision-making theory and practice are covered in the course. Students will learn why firms prioritize shareholder wealth. Investment, finance, dividends, and risk management are also crucial to wealth creation, which students will learn.
3. STUDY HOURS

4. ROLE IN CURRICULUM
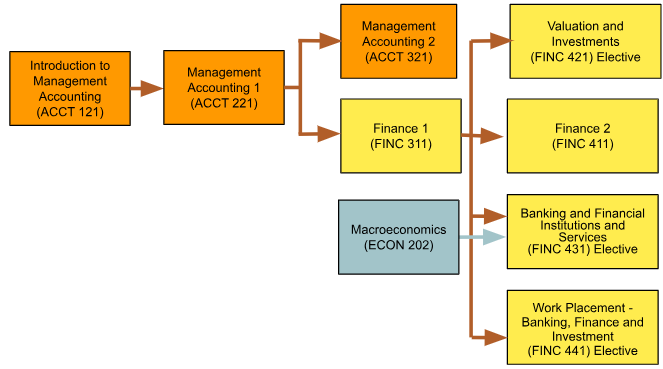
Prerequisites:
Students must have completed Finance 1 (FINC 311) before attempting this course.
The learning outcomes for this course cover four main areas in corporate finance: investment decisions, financing decisions, dividend policy decisions, and working capital management. On successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
| Knowledge | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
|---|---|---|
| Explain how economy affects finance (CK1) Explain how economic conditions affect financial management and corporate finance management theory, concepts, and practice. |
Understand | PK1 |
| Discuss how companies create value (CK2) Discuss how financial decisions in investment, finance, dividends, working capital, and risk management can maximize shareholder wealth. |
Understand | PK2 |
| Cognitive Skills | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
| Examine financial strategies and decisions (CC1) Carry out effective investment appraisal, working capital, and finance analysis to help businesses make informed decisions to maximize shareholder wealth. |
Analyze | PC1 |
| Evaluate corporate funding sources and costs (CC2) Assess different corporate finance sources and their costs to plan business expansion and maximize shareholder wealth. |
Evaluate | PC1 |
| Communication, Information Technology, and Numerical Skills | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
| Use Microsoft Excel (CCIT1) Use Microsoft Excel software to prepare capital budgets using different investment appraisal techniques. |
Apply | PCIT2 |
| Interpersonal Skills and Responsibilities | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
| Work ethically (CIP1) Apply ethical behavior as a finance manager in accordance with the ACCA Code of Ethics and Conduct. |
Characterize | PIP2 |
Grades will be determined based on the following assessments and score allocations:
| SKILL | Assessment | Skill Weighting for Grade |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participation | In-class tests | Case Study | Project | Midterm Exam | Final Exam | |||
| Explain how economy affects finance (CK1) | 20% | 50% | 30% | 15% | ||||
| Discuss how companies create value (CK2) | 20% | 40% | 40% | 15% | ||||
| Examine financial strategies and decisions (CC1) | 60% | 40% | 30% | |||||
| Evaluate corporate funding sources and costs (CC2) | 70% | 30% | 30% | |||||
| Use Microsoft Excel (CCIT1) | 20% | 20% | 30% | 30% | 5% | |||
| Work ethically (CIP1) | 100% | 5% | ||||||
The primary instructional approach of this course involves lectures, case study analysis, and problem application. The case studies used come from previous exams for the Financial Management paper (F9) released by the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA), as well as case studies from the Harvard Business School. The readings that have been designated will facilitate the process of learning and function as a point of reference for the content that has been discussed during class. During the teaching period, there will be an equal amount of time for lectures and hands-on activities like case studies, problem-solving activities, and going over the answers.
During the course, there is one project:
| Assignment: | Sustainability Reporting in Cambodia (CC2, CCIT1 & CIP2) |
| Work Group: | Group of 4 |
| Output format: | APA Format Report, Presentation |
| Language: | English |
|
Description:
|
There has been growing demand for greater corporate transparency not just in financial accounting reporting but also in management actions that would have an impact on companies’ sustainability over the long term, such as environmental and social impact, with the current trend moving towards sustainability reporting. This assignment aims to examine the development and evolution of sustainability reporting practices in Cambodia to identify the current practice and trend of reporting and the level of awareness of sustainability reporting in Cambodia. Assignment Rubric: |
The course targets the study plan below. Implementation may vary somewhat depending on the progress and needs of students. For example, some topics may be allocated more or less than 1.5 hours.
| Lesson Learning Outcomes | Teaching and Learning Activities, Assessment | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
The financial management and objectives
|
Lecture Demonstration of financial management Group exercise on the reason for disposing of surplus assets.Reading: BPP Text Chapter 1 pp 1-23 |
| 2 |
The financial management and objectives
|
Lecture Demonstration measuring achievement of objective Group exercise on investor and profitability ratiosReading: BPP Text Chapter 1 pp 1-23 |
| 3 |
The financial management and objectives
|
Lecture Group case study of Taing Chan Lim Co Group drill and practice on measures of Effectiveness/KPIsReading: BPP Text Chapter 1 pp 1-23 |
| 4 |
The economic environment
|
Lecture Demonstration on stakeholder’s theoryReading: BPP Text Chapter 2 pp 25-44 |
| 5 |
The economic environment
|
Lecture Demonstration on government economic objectivesReading: BPP Text Chapter 2 pp 25-44 |
| 6 |
The economic environment
|
Lecture Discussion the effect of fiscal policy to economicReading: BPP Text Chapter 2 pp 25-44 |
| 7 |
Investment decisions using non-discounted cash flow methods
|
Lecture Demonstration of concept time value of money and investment appraisal method with non-discounted cash flow Solving exam question on determining the proposed investment based on ROCE and ARRReading: BPP Text Chapter 5 pp 106-134 |
| 8 |
Investment appraisal using discounted cash flow methods
|
Lecture Demonstration of discount cash flow Group drill and practice on new project NPVReading: BPP Text Chapter 5 pp 106-134 |
| 9 |
Investment appraisal using discounted cash flow methods (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion on concept of IRR Group exercise on the proposed investment based on NPV and IRRReading: BPP Text Chapter 5 pp 106-134 |
| 10 |
Capital budgeting under inflation and taxation
|
Lecture Discussion on relevant and non-relevant cash flow and inflationReading: BPP Text Chapter 6 pp 135-156 |
| 11 |
Capital budgeting under inflation and taxation (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstration of capital allowancesReading: BPP Text Chapter 6 pp 135-156 |
| 12 |
Capital budgeting under inflation and taxation (continued)
|
Lecture Solving exam question on the proposed investment with nominal cost of discountReading: BPP Text Chapter 6 pp 135-156 |
| 13 |
Project appraisal under risk
|
Lecture Demonstration of risk and uncertainty analysisReading: BPP Text Chapter 7 pp 157-200 |
| 14 |
Project appraisal under risk (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstration of sensitivity and probability analysis Group exercise on measure sensitivity of projectReading: BPP Text Chapter 7 pp 157-200 |
| 15 |
Specific investment decisions (continued)
|
Lecture Group problem on capital rationing and ostponabilityReading: BPP Text Chapter 8 pp 173-200 |
| 16 |
Sources of finance
|
Lecture Discussion on different sources of finance Group problem on debt valuationReading: BPP Text Chapter 9 & 10 pp 201-232 |
| 17 |
Sources of finance (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion on right issues Group exercise on the effect of right issues to shareholder’s wealthReading: BPP Text Chapter 9 & 10 pp 201-232 |
| 18 |
Dividend policy
|
Lecture Demonstrate and didactic questioning on dividend policiesReading: BPP Text Chapter 9 & 10 pp 201-232 |
| 19 |
Dividend policy (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstrate of dividend policies Group case study analysisReading: BPP Text Chapter 9 & 10 pp 201-232 |
| 20 |
Cost of capital
|
Lecture Discussion and calculate cost of equity by CAPM and DVM Group problem on cost of equity calculationReading: BPP Text Chapter 11 pp 233-261 |
| 21 |
Cost of capital (continued)
|
Lecture Calculate different cost of debtReading: BPP Text Chapter 11 pp 233-261 |
| 22 |
Cost of capital (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstrate of WACC Didactic questioning on project specific cost of capital Group exercise on WACC calculationReading: BPP Text Chapter 11 pp 233-261 |
| 23 |
Gearing and capital structure
|
Lecture Calculate the different types of gearing Group exercise on the effect of new investment to gearingReading: BPP Text Chapter 12 pp 263-292 |
| 24 |
Gearing and capital structure (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstration of financial structureReading: BPP Text Chapter 12 pp 263-292 |
| 25 |
Gearing and capital structure (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstration of M&M with and without tax Group case study analysis on M&M PIZZAReading: BPP Text Chapter 12 pp 263-292 |
| 26 |
Introduction to working capital management
|
Lecture Demonstration of working capital component Group case study on working capital ratiosReading: BPP Text Chapter 3 pp 45-106 |
| 27 |
Introduction to working capital management
|
Lecture Demonstration of working capital component Group case study on working capital ratiosReading: BPP Text Chapter 3 pp 45-106 |
| 28 |
Managing working capital
|
Lecture Demonstration of managing inventory Group problem on policy to minimize inventory costReading: BPP Text Chapter 3 pp 45-106 |
| 29 |
Managing working capital (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstration of managing inventory Solving exam question on inventory managementReading: BPP Text Chapter 3 pp 45-106 |
| 30 |
Managing working capital (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstration of receivable management Group drill and practice on settlement discount decisionReading: BPP Text Chapter 3 pp 45-106 |
| 31 |
Financing working capital
|
Lecture Demonstration of receivable management Group drill and practice on settlement discount decisionReading: BPP Text Chapter 3 pp 45-106 |
| 32 |
Financing working capital (continued)
|
Lecture Demonstration of cash management Group drill and practice on cash flow forecastReading: BPP Text Chapter 4 pp 78-106 |
| 33 |
Financing working capital (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion of diversification of risk and treasury managementReading: BPP Text Chapter 4 pp 78-106 |
| 34 |
Business valuation
|
Lecture Discussion on methods to value businessReading: BPP Text Chapter 13 293-327 |
| 35 |
Business valuation (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion on methods to value business Solving exam question on method of business valuation that appropriateReading: BPP Text Chapter 13 293-327 |
| 36 |
Business valuation (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion on methods to value business Solving exam question on method of business valuation that appropriateReading: BPP Text Chapter 13 293-327 |
| 37 |
Business valuation (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion on methods to value business Solving exam question on method of business valuation that appropriateReading: BPP Text Chapter 13 293-327 |
| 38 |
Business valuation (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion on methods to value business Solving exam question on method of business valuation that appropriateReading: BPP Text Chapter 13 293-327 |
| 39 |
Foreign currency
|
Lecture Demonstration of exchange rate Group exercise on conversion of foreign currencyReading: BPP Text Chapter 14 329-361 |
| 40 |
Foreign currency risk (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion of method to hedge foreign exchange rate riskReading: BPP Text Chapter 14 329-361 |
| 41 |
Foreign currency risk (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion of international fisher effect and money market hedge Group exercise on foreign exchange risk whether to use forward or money market hedgeReading: BPP Text Chapter 14 329-361 |
| 42 |
Foreign currency risk (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion of international fisher effect and money market hedge Group exercise on foreign exchange risk whether to use forward or money market hedgeReading: BPP Text Chapter 14 329-361 |
| 43 |
Foreign currency risk (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion of international fisher effect and money market hedge Group exercise on foreign exchange risk whether to use forward or money market hedge Reading: BPP Text Chapter 14 329-361 |
| 44 |
Foreign currency risk (continued)
|
Lecture Discussion of international fisher effect and money market hedge Group exercise on foreign exchange risk whether to use forward or money market hedgeReading: BPP Text Chapter 14 329-361 |
| 45 | Team Presentations – Complete Report (CK1, CC1, CCIT1, CIP1) | Team presentations and feedback |
| 46 | Team Presentations – Complete Report (CK1, CC1, CCIT1, CIP1) | Team presentations and feedback |
| 47 | Team Presentations – Complete Report (CK1, CC1, CCIT1, CIP1) | Team presentations and feedback |
| 48 | Team Presentations – Complete Report (CK1, CC1, CCIT1, CIP1) | Team presentations and feedback |
| 49 | Team Presentations – Complete Report (CK1, CC1, CCIT1, CIP1) | Team presentations and feedback |
| 50 | Exam Review |
Textbooks
References