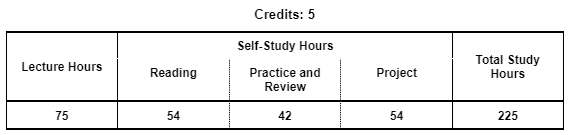
| 1 |
Introduction
Accounting for Management
- Describe the purpose and role of cost and management accounting within an organization. (CK1)
- Compare and contrast financial accounting with cost and management accounting. (CK1)
|
Lecture
Examples
Reading: Chapter 1 |
| 2 |
Accounting for Management (continued)
- Identify and explain the attributes of good information. (CK1)
- Explain the limitations of management information in providing guidance for managerial decision-making. (CK1)
|
Lecture
Class activity using MCQs
Reading: Chapter 1 |
| 3 |
Sources of data and analysis data
- Describe sources of information from within and outside the organization (including government statistics, financial press, professional or trade associations, quotations, and price lists). (CK1)
- Explain the uses and limitations of published information/data (including information from the internet). (CK1)
|
Lecture
Examples
Reading: Chapter 2 |
| 4 |
Sources of data and analysis data (Cont.)
- Describe the impact of the general economic environment on costs/revenues. (CK1)
- Explain sampling techniques (random, systematic, stratified, multistage, cluster, and quota). (CK1)
|
Lecture
Examples
Reading: Chapter 2 |
| 5 |
Sources of data and analysis data (Cont.)
- Choose an appropriate sampling method in a specific situation. (CK1
|
Lecture
Examples
Reading: Chapter 2 |
| 6 |
Presenting Information
- Prepare written reports representing management information in suitable formats according to purpose. (CCIT1)
- Present information using tables, charts, and graphs (bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and scatter graphs). (CCIT1)
- Interpret information (including tables, charts, and graphs) presented in management reports. (CCIT1)
|
Lecture
Class Activity with MCQs
Reading: Chapter 3
|
| 7 |
Cost Classification
- Explain and illustrate production and non-production costs. (CC1)
- Describe the different elements of non-production costs – administrative, selling, distribution, and finance. (CC1)
- Describe the different elements of production costs – materials, labor, and overheads. (CC1)
-
|
Lecture
Class Activities with Problem
Solving Questions
Reading: Chapter 4
|
| 8 |
Cost Classification (continued)
- Explain and illustrate with examples classifications used in the analysis of the product/service costs including by function, direct and indirect, fixed and variable, stepped fixed and semi-variable costs. (CC1)
- Explain and illustrate the concept of cost objects, cost units and cost centres. (CC1)
- Describe the differing needs for information of cost, profit , investment and revenue centre manager. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Group activity on costs
classification.
Reading: Chapter 4 |
| 9 |
Cost Classification (continued)
- Explain and illustrate with examples classifications used in the analysis of the product/service costs, including by function, direct and indirect, fixed and variable, stepped fixed and semi-variable costs. (CC1)
- Describe and illustrate graphically different types of cost behavior. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Group activity on costs classification.
Reading: Chapter 4
|
| 10 |
Cost Classification (continued)
- Use high-low analysis to separate the fixed and variable elements of total costs, including situations involving semi-variable and stepped fixed costs and changes in the variable cost per unit. (CC1)
- Explain the structure of linear functions and equations. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Quiz on Chapters 3 a & b (MCQs)
Reading: Chapter 4
|
| 11 |
Accounting for Materials
- Describe the different procedures and documents necessary for the ordering, receiving, and issuing of materials from the inventory. (CC1)
- Interpret the entries and balances in the material inventory account. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions.
Reading: Chapter 5
|
| 12 |
Accounting for Materials (continued)
- Produce calculations to minimize inventory costs when inventory is gradually replenished. (CC1)
- Describe and apply appropriate methods for establishing reorder levels where demand in the lead time is constant. (CC1)
- Calculate the value of closing inventory and material issues using LIFO, FIFO, and average methods. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 5
Reading: Chapter 5
|
| 13 |
Accounting for Labour
- Calculate direct and indirect costs of labor. (CC1)
- Explain the methods used to relate input labor costs to work done. (CC1)
- Prepare the journal and ledger entries to record labor cost inputs and outputs. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 6
|
| 14 |
Accounting for Labour (continued)
- Calculate the level, and analyze the costs and causes, of labor turnover. (CC1)
- Explain and calculate labor efficiency, capacity and production volume ratios. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 6
Reading: Chapter 6
|
| 15 |
Accounting for Overheads
- Describe the procedures involved in determining production overhead absorption rates. (CC1)
- Allocate and apportion production overheads to cost centre using an appropriate basis. (CC1)
- Reapportion service cost centre costs to production cost centres (using reciprocal method where service cost centres work for each other). (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 7
|
| 16 |
Accounting for Overheads (continued)
- Select, apply, and discuss appropriate bases for absorption rates. (CC1)
- Prepare journal and ledger entries for manufacturing overheads incurred and absorbed. (CC1)
- Calculate and explain the under and over-absorption of overheads. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 7
Reading: Chapter 7
|
| 17 |
Absorption and Marginal Costing
- Explain the importance of, and apply, the concept of contribution. (CC1)
- Demonstrate and discuss the effect of absorption and marginal costing on inventory valuation and profit determination. (CC1)
- Calculate profit and loss under absorption and marginal costing. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Group work on research on P/L using absorption and marginal costing.
Reading: Chapter 8
|
| 18 |
Absorption and Marginal Costing (continued)
- Reconcile the profits or losses calculated under absorption and marginal costing. (CC1)
- Describe the advantages and disadvantages of absorption and marginal costing. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 8
Reading: Chapter 8
|
| 19 |
Job, Batch and Service Costing
- Describe the characteristics of job and batch costing. (CC1)
- Describe the situations where the use of job or batch costing would be appropriate. (CC1)
- Prepare cost records and accounts in job and batch costing situations. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 9
|
| 20 |
Job, Batch and Service Costing (continued)
- Identify situations where the use of service/operation costing is appropriate. (CC1)
- Illustrate suitable unit cost measures that may be used in different service/operation situations. (CC1)
- Carry out service cost analysis in simple service industry situations. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Quiz on Chapter 9
Reading: Chapter 9
|
| 21 |
Process Costing
- Describe the characteristics of process costing. (CC1)
- Describe the situations where the use of process costing would be appropriate. (CC1)
- Prepare process accounts, involving normal and abnormal losses and abnormal gains. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 9
|
| 22 |
Process Costing (continued)
- Prepare process accounts in situations where work remains incomplete. (CC1)
- Prepare process accounts where losses and gains are identified at different stages of the process. (CC1)
- Distinguish between by-products and joint products. (CC1)
- Prepare process accounts in situations where by-products and/or joint products occur. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 9
Reading: Chapter 9
|
| 23 |
Service and operation costing
- Identify situations where the use of service/operating costing is appropriate (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 10
|
| 24 |
Service and operation costing (continued)
- Illustrate suitable unit cost measures that may be used in different service/operation situations (CC1)
- Carry out service cost analysis in simple service industry situations (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 10
Reading: Chapter 10
|
| 25 |
Alternative Costing principles
- Explain activity-based costing (ABC), target costing, life cycle costing, and total quality management (TQM) as alternative cost management techniques. (CC2)
- Differentiate ABC, target costing, and life cycle costing from the traditional costing techniques (calculations are not required). (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 11
|
| 26 |
Forecasting
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using the high-low method to estimate the fixed and variable elements of costing. (CC2)
- Construct scatter diagrams and lines of best fit. (CC2)
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of linear regression analysis. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 12
|
| 27 |
Forecasting (continued)
- Explain the principles of time series analysis (Cyclical, trend, seasonal variation, and random elements). (CC2)
- Calculation of trend, including the use of regression coefficients. (CC2)
- Calculate simple index numbers for one or more variables. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 12
|
| 28 |
Budgeting
- Explain why organizations use budgeting. (CC2)
- Describe the planning and control cycle in an organization. (CC2)
- Explain and illustrate ‘what if’ analysis and scenario planning. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 13
|
| 29 |
Budgeting
- Explain the importance of flexible budgets in control. (CC2)
- Explain the disadvantages of fixed budgets in control. (CC2)
- Identify situations where fixed or flexible budgetary control would be appropriate. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 13
Reading: Chapter 13
|
| 30 |
Budgeting
- Explain the administrative procedures in the budgeting process. (CC2)
- Describe the stages in the budgeting process (includes relevant data, planning and agreeing on draft budgets, and the purpose of forecasts and how they link to budgeting.) (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 13
|
| 31 |
Budgeting
- Prepare functional budgets (production, raw materials usage, and purchases, labor, variable, and fixed overheads.) (CC3)
- Prepare cash budgets. (CC2)
- Prepare master budgets (statement of profit or loss and statement of financial position). (CC3)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 13
|
| 32 |
Budgeting
- Explain the importance of motivation in performance management. (CC2)
- Identify factors in a budgetary planning and control system that influence motivation (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 13
|
| 33 |
Budgeting
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a participative approach to budgeting. (CC2)
- Explain top-down, and bottom-up approaches to budgeting. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 13
Reading: Chapter 13
|
| 34 |
Capital Budgeting
- Discuss the importance of capital investment planning and control. (CC2)
- Define and distinguish between capital and revenue expenditure. (CC2)
- Outline the issues to consider and the steps involved in the preparation of a capital expenditure budget.(CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 14
|
| 35 |
Capital Budgeting
- Explain and illustrate the difference between simple and compound interest, and between nominal and effective interest rates. (CC2)
- Explain and illustrate compounding and discounting. (CC2)
- Explain the distinction between cash flow and profit and the relevance of cash flow to capital investment appraisal. (CC2)
- Identify and evaluate relevant cash flows for individual investment decisions. (CC2)
- Explain and illustrate the net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR) methods of discounted cash flow. (CC4)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 14
|
| 36 |
Capital Budgeting (continued)
- Calculate present value using annuity and perpetuity formulate. (CC4)
- Calculate NPV, IRR, and payback (discounted and non discounted) (CC4)
- Interpret the results of NPV, IRR, and payback calculates of investment viability. (CC4)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Quiz on Chapter 14
Reading: Chapter 14
|
| 37 |
Standard Costing
- Explain the purpose and principles of standard costing. (CC3)
- Explain and illustrate the difference between standard, marginal and absorption costing. (CC1)
- Establish the standard cost per unit under absorption and marginal costing.(CC1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 15
|
| 38 |
Standard Costing
- Variance Calculations and Analysis
- Calculate materials total, price, and usage variance. (CC3)
- Calculate labor total, rate, and efficiency variance. (CC3)
- Calculate variance overhead total, expenditure and efficiency.(CC3)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 15
|
| 39 |
Standard Costing
Budgetary control and reporting
- Calculate sample variances between flexed budget, fixed budget and actual sales, costs and profits. (CC3)
- Discuss the relative significance of variance. (CC3)
- Explain potential action to eliminate variances. (CC3)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 15
|
| 40 |
Standard Costing
- Reconcile budget profit with actual profit under standard absorption costing. (CC1)
- Reconcile budgeted profit or contribution with actual profit or contribution under standard marginal costing. (CC1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 15
|
| 41 |
Performance Measurement
- Discuss the purpose of mission statements and their role in performance measurement. (CC2)
- Discuss the purpose of strategic and operational and tactical objectives and their role in performance measurement. (CC2)
- Discuss the impact of economic and market conditions on performance measurement. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 16
|
| 42 |
Performance Measurement
- Establish critical success factors and key performance indicators in a specific situation. (CC2)
- Discuss the role of benchmarking in performance measurement. (C2)
- Discuss and calculate measures if financial performance (profitability, liquidity, activity and gearing) and non-financial measures. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 16
|
| 43 |
Performance Measurement
- Describe performance indicator for financial success., customer satisfaction, process efficiency and growth. (CC2)
- Explain the concepts of economy, efficiency and effectiveness. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 16
|
| 44 |
Performance Measurement
- Describe performance measures which would be suitable in contract and process costing environments. (CC2)
- Describe measures of performance utilisation in service and manufacturing environments. (CC2)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 16
|
| 45 |
Spreadsheets
- Explain the role, features and uses of a spreadsheet package. (CCIT1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 17
|
| 46 |
Spreadsheets
- Identify applications for computer spreadsheets and their use in cost management (CCIT1)
|
Lecture
Class Activities using sample questions
Reading: Chapter 17
|
| 47 |
Practical Questions & Answers |
Reading: Chapter 18 |
| 48 |
Practical Questions & Answers |
Reading: Chapter 18 |
| 49 |
Practical Questions & Answers |
Reading: Chapter 19 |
| 50 |
Practical Questions & Answers |
Reading: Chapter 19 |
| |
Guest Lecture
- Budgeted planning
- Financial and nonfinancial performance measurement
|
Lecture |