1. COURSE DESCRIPTION
The syllabus for audit theory starts with an introduction to the nature and purpose of an audit, including the duties and liability of auditors, and the regulation that auditors must adhere to. The syllabus then covers the areas relating to the process of an audit of financial statements starting with audit planning and risk assessment, recording and evaluating internal control, as well as tests of controls, audit evidence, and the use of substantive procedures. The final section deals with audit completion including the audit report.
2. REASON FOR THE COURSE
A statutory auditor must be able to demonstrate technical skills in auditing the financial statements in accordance with the International Standards on Auditing (CISAs). Therefore, program graduates will be auditing the financial statements prepared by the management to express a legal opinion on the financial statements whether they present fairly in all material respects and in accordance with the applicable financial reporting framework.
3. STUDY HOURS
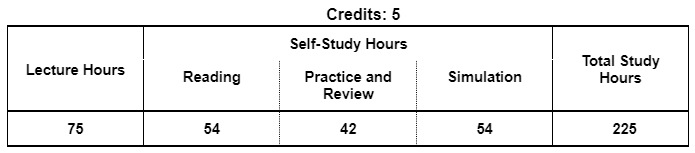
4. ROLE IN CURRICULUM
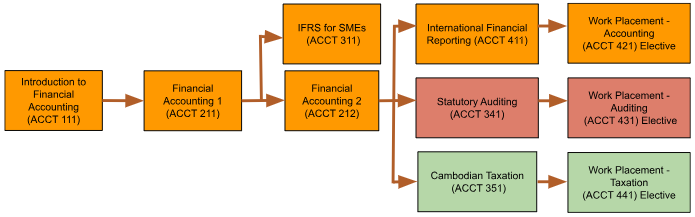
Auditing is the first course to introduce the fundamental knowledge on external audit processes for the bachelor of accounting and finance, building on existing financial accounting studies.
Prerequisites:
Students must have completed Financial Accounting 1 (ACCT 211) and Financial Accounting 2 (ACCT 212).
On successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
| Knowledge | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
|---|---|---|
| Explain the Principles of Internal Control (CK1) Explain the principles of internal control and the features of information systems. |
Understand | PC2 |
| Describe Audit Procedures and Evidence (CK2) Describe audit procedures and audit evidence required to meet the objectives of an audit and apply International Standards on Auditing (ISAs). |
Understand | PC2 |
| Cognitive Skills | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
| Interpret the Regulatory Framework & Code of Ethics (CC1) Interpret the purpose and scope of an audit and its regulatory framework as well as uphold the fundamental principles of the ACCA code of ethics and conduct to the duties of an auditor. |
Apply | PC2 |
| Assess Audit Risks (CC2) Assess the audit risks by understanding the entity and its environment in order to plan for an audit |
Analyze | PC2 |
| Perform the Audit Completion Process (CC3) Perform the audit completion process in order to form an audit opinion. |
Apply | PC2 |
| Communication, Information Technology, and Numerical Skills | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
| Utilize Technology in the Audit Process (CCIT1) Utilize Word software and spreadsheets to facilitate the preparation of learning papers on case studies, assignments, quizzes, and mock exams. |
Apply | PCIT2 |
| Interpersonal Skills and Responsibilities | Level of Learning | Related PLO |
| Collaborate in Audit Simulation (CIP1) Participate in a team to prepare audit programs for real entities and/or audit simulations. |
Create | PIP1 |
Grades will be determined based on a grading score, calculated using the following assessments and score allocations:
| SKILL | Assessment |
Weighting for Grade |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participation | In-class tests | Controlled Case Studies | Simulation | Final Exam | |||
| Explain the Principles of Internal Control (CK1) | 20% | 20% | 60% | 5% | |||
| Describe Audit Procedures and Evidences (CK2) | 30% | 35% | 35% | 20% | |||
| Interpret the Regulatory Framework & Code of Ethics (CC1) | 30% | 10% | 60% | 20% | |||
| Assess Audit Risks (CC2) | 40% | 30% | 30% | 25% | |||
| Perform the Audit Completion Process (CC3) | 35% | 65% | 20% | ||||
| Utilize Technology in the Audit Process (CCIT1) | 15% | 55% | 30% | 5% | |||
| Collaborate in Audit Simulation (PIP 1) | 40% | 60% | 5% | ||||
This course is primarily lecture and assignment-based; assigned homework and in-class tests will support learning to material covered in class. The class will be devoted to lectures, exercises, and in-class tests.
During the course, the following Course Outputs are required:
| 1 – Learning Paper on Controlled Case Studies: (CK1 CK2 CC1 CC2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case Study no. 1 on Audit Planning and Risk Assessments | ||||
| Case Study no. 2 on Internal Controls and Audit Procedures | ||||
| 2 – Assignment: Audit Simulation (CK2 PK2 CC2 CC3 CCIT1 CIP1) | ||||
| Work Group: | Group | |||
| Output format: | Presentation Slide and Working Papers | |||
| Language: | English | |||
| Description: |
Students will be assigned to participate in the audit simulation. They will be in charge of an audit engagement for a particular client and will be given a list of tasks to complete in each phase. They will start the engagement by understanding the client and its environment until the completion stage in which the auditor will issue an audit report. At the end of the term, students are required to do a presentation about their work from each phase, complete the peer assessment, and write a self-reflection about this simulation. Assignment Rubric |
|||
The course targets the 50 lessons in the study plan below. Each lesson is 1.5 class hours each; there are a total of 75 class hours (excluding 3 hours of Final Review) The study plan below describes the learning outcome for each lesson, described in terms of what the student should be able to do at the end of the lesson. Readings should be done by students as preparation before the start of each class. Implementation of this study plan may vary somewhat depending on the progress and needs of students.
| Lesson Learning Outcomes | Teaching and Learning Activities, Assessment | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Introduction
|
Lecture Discussion – Kahoot Video |
| 2 |
Business environment
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 1 Demonstration of an audit report Oral questions HomeworkReading: Chapter 1 (Kaplan) |
| 3 |
Business environment (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 1 Demonstration of an audit report Oral questions QuizReading: Chapter 1 (Kaplan) |
| 4 |
Auditors responsibilities
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 2 Demonstration of director’s responsibilities – Kahoot HomeworkReading: Chapter 4 (Kaplan) |
| 5 |
Auditors responsibilities (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 2 Demonstration of director’s responsibilities QuizReading: Chapter 4 (Kaplan) |
| 6 |
Audit regulation
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 3 Discussion Case Study HomeworkReading: Chapter 2 (Kaplan) Technical Paper |
| 7 |
The ACCA Code of Ethics and Conduct
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 3 Discussion – Kahoot Didactic questioningReading: Chapter 2 (Kaplan) |
| 8 |
The ACCA Code of Ethics and Conduct for Auditors
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 3 Discussion – KahootReading: Chapter 2 (Kaplan) |
| 9 |
Audit regulation (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 3 Discussion – Kahoot Drill & Practice QuizReading: Chapter 2 (Kaplan) |
| 10 |
Auditor appointment
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 4 Discussion – Kahoot Concept mapping HomeworkReading: Chapter 3 (Kaplan) |
| 11 |
Auditor appointment (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 4 Discussion – Kahoot Drill & Practice QuizReading: Chapter 3 (Kaplan) |
| 12 |
Risk assessment
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 5 Didactic questioning Drill and practice HomeworkReading: Chapter 5 (Kaplan) Technical Paper |
| 13 |
Risk assessment (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 5 Didactic questioning Drill and practice KahootReading: Chapter 5 (Kaplan) |
| 14 |
Risk assessment (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 5 Concept mapping Case Study no. 1Reading: Chapter 5 (Kaplan) |
| 15 |
Risk assessment (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 5 Concept mappingReading: Chapter 5 (Kaplan) |
| 16 |
Risk assessment (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 5 Concept mappingReading: Chapter 5 (Kaplan) |
| 17 |
Risk assessment (continued)
|
Lecture Concept mapping QuizReading: Chapter 5 (Kaplan) |
| 18 |
Audit planning
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 6 Discussion – Kahoot Didactic questioning HomeworkReading: Chapter 5,8,14 (Kaplan) |
| 19 |
Audit planning (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 6 Discussion – Kahoot Didactic questioning Drill and practiceReading: Chapter 5,8,14 (Kaplan) Technical Paper |
| 20 |
Audit planning (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 6 Concept mapping Compare and contrastReading: Chapter 5,8,14 (Kaplan) |
| 21 |
Audit planning (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 6 Discussion – Kahoot Didactic questioning Drill and practice HomeworkReading: Chapter 5,8,14 (Kaplan) |
| 22 |
Audit planning (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 6 Discussion – Kahoot Didactic questioning Drill and practiceReading: Chapter 5,8,14 (Kaplan) Technical Paper |
| 23 |
Audit planning (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 6 Didactic questioning Drill and practice QuizReading: Chapter 5,8,14 (Kaplan) |
| 24 |
nternal control evaluation
|
Lecture Discussion – KahootReading: Chapter 7 Technical Paper |
| 25 |
nternal control evaluation (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 7 Didactic questioning Discussion – KahootReading: Chapter 6 (Kaplan) |
| 26 |
Internal control evaluation (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 7 Didactic questioning Discussion – KahootReading: Chapter 6 (Kaplan) |
| 27 |
Internal control evaluation (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 7 Didactic questioning Discussion QuizReading: Chapter 6 (Kaplan) |
| 28 |
Tests of control: income and expenditures cycles
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 8 Didactic questioning Demonstration HomeworkReading: Chapter 7 (Kaplan) |
| 29 |
Tests of control: income and expenditures cycles (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 8 Didactic questioning DemonstrationReading: Chapter 7 (Kaplan) |
| 30 |
Tests of control: income and expenditures cycles (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 8 Drill & Practice Quiz Case Study no. 2Reading: Chapter 7 (Kaplan) |
| 31 |
Analytical procedures and estimates
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 10 Compare and contrast exercise HomeworkReading: Chapter 9 (Kaplan) Technical Paper |
| 32 |
Analytical procedures and estimates (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 10 QuizReading: Chapter 9 (Kaplan) |
| 33 |
Non-current assets
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 10, 11 Discussion – Kahoot HomeworkReading: Chapters 7, 10 (Kaplan) |
| 34 |
Non-current assets (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 10,11 Discussion – KahootReading: Chapters 7, 10 (Kaplan) |
| 35 |
Non-current assets (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 10, 11 Discussion – KahootReading: Chapters 7, 10 (Kaplan) |
| 36 |
Non-current assets (continued)
|
Drill and Practice QuizReading: Chapters 7, 10 (Kaplan) |
| 37 |
Inventories
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 9,12 Video Concept mapping HomeworkReading: Chapters 7, 11 (Kaplan) |
| 38 |
Inventories (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 9,12 Discussion – KahootReading: Chapters 7, 11 (Kaplan) |
| 39 |
Inventories (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 9,12 Discussion – KahootReading: Chapters 7, 11 (Kaplan) |
| 40 |
Inventories (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 9,12 Drill & Practice QuizReading: Chapters 7, 11 (Kaplan) |
| 41 |
Accounts receivable and cash
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 9,13 HomeworkReading: Chapters 7, 12 (Kaplan) |
| 42 |
Accounts receivable and cash (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 9,13 Discussion – KahootReading: Chapters 7, 12 (Kaplan) |
| 43 |
Accounts receivable and cash (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapters 9,13 Drill & Practice QuizReading: Chapters 7, 12 (Kaplan) |
| 44 |
Liabilities
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 9,14 Discussion – Kahoot HomeworkReading: Chapter 7, 13 (Kaplan) |
| 45 |
Liabilities (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 9,14 Discussion – KahootReading: Chapter 7, 13 (Kaplan) |
| 46 |
Liabilities (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 9,14 Drill and practice Quiz Case Study no. 2Reading: Chapter 7, 13 (Kaplan) |
| 47 |
Forming an audit judgement
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 15 Didactic questioning HomeworkReading: Chapter 15 (Kaplan) |
| 48 |
Forming an audit judgement (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 15 Drill & Practice QuizReading: Chapter 15 (Kaplan) |
| 49 |
The external audit opinion
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 16 Discussion – Kahoot HomeworkReading: Chapter 16, 17 (Kaplan) Technical Paper |
| 50 |
The external audit opinion (continued)
|
Lecture Notes – Chapter 16 Drill & Practice QuizReading: Chapter 16, 17 (Kaplan) |
| Total Hours : 75 hours | ||
Textbooks
References
*latest applicable version